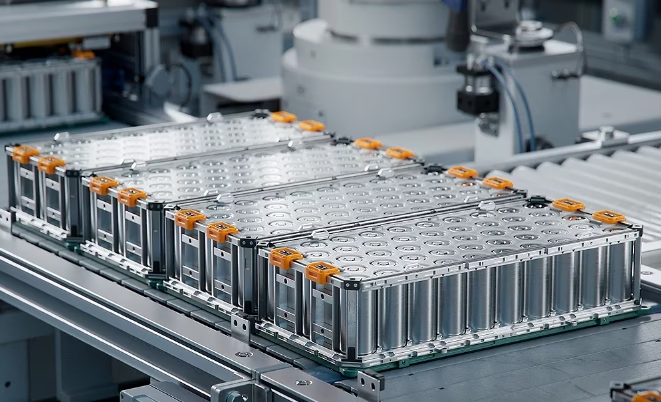
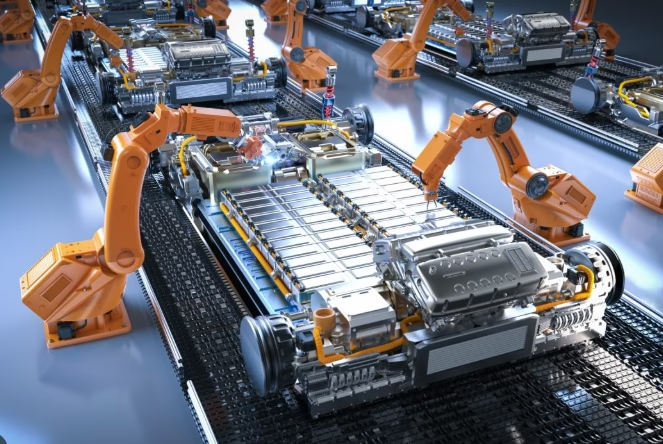
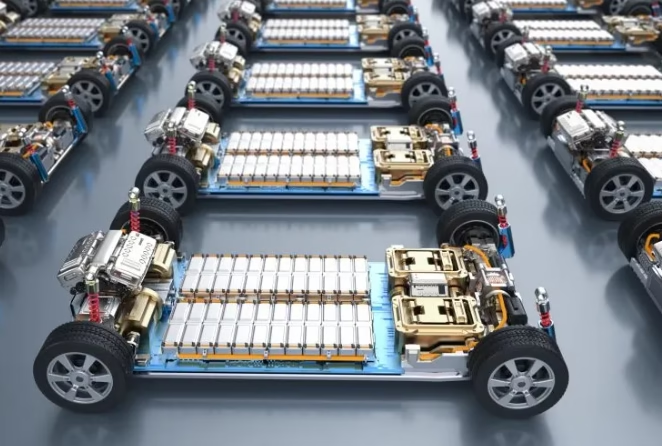
With the widespread adoption of high-voltage fast-charging accessories, how can battery longevity and charging safety be balanced? The proliferation of high-voltage fast-charging technology has delivered more efficient energy replenishment for new energy vehicles, yet this technological advancement also poses dual challenges to battery lifespan and charging safety.
Current technology employs graphite fast-ion loops to create high-speed conductive pathways on the anode surface, boosting lithium-ion insertion efficiency by several orders of magnitude. Combined with amorphous lithium-silicon alloy interfacial layers, this significantly increases dendrite penetration resistance, mitigating safety risks at their source.
As charging power increases, internal battery temperatures rise substantially. High temperatures accelerate electrode material degradation and electrolyte decomposition. Integrating liquid cooling systems with phase-change materials maintains battery temperature within minimal variations, preventing localized overheating.
Battery management systems must respond within milliseconds, continuously monitoring each cell’s voltage and temperature to instantly adjust charging strategies upon detecting anomalies. Communication protocols between charging stations and vehicles require upgrades to ensure real-time data exchange during charging, eliminating overcharge risks caused by information delays.
Maintaining batteries at full charge for extended periods accelerates electrolyte decomposition. Limiting charging to a specific percentage significantly extends cycle life. For daily use, prioritize slow charging during off-peak hours and perform slow charges monthly to calibrate the battery meter.
Low temperatures reduce battery activity, a short drive before charging can warm the battery. In high temperatures, avoid direct sunlight during charging and reduce charging power if necessary. For vehicles in long-term storage, maintain the battery within a reasonable charge range and periodically recharge to prevent deep discharge.
With the widespread adoption of high-voltage fast-charging accessories, how can battery longevity and charging safety be balanced? The application of solid-state electrolytes fundamentally eliminates dendrite growth issues, enabling higher charging power. During the transition phase, high-voltage fast-charging technology can effectively extend battery life while ensuring safety.












Leave a Reply